Hi—this is Kisan from The Cloud Handbook. Each week, I write about Cloud, DevOps, Systems Design deep dives and community update around it. If you have not subscribed yet, you can subscribe here.
In this episode of The Cloudhandbook, we are discussing about some caching techniques used in software engineering.
What is Caching?
Caching is a technique to store frequently accessed data temporarily in a high speed storage for faster retrieval.
It is an essential part of modern web applications to enhance system performance by reducing the response time, reduct load on server and database, reduct network costs.
Benefits of Caching
Reduce response time: When the user requests for any webpage or data, caching helps return the response from the nearest and fastest cache, reducing the response time and increasing application performance.
Reduce server load: Caching helps to reduce server load returning the data and assets directly from the cache without the need for running server scripting or database queries.
Reduce network costs: Use of caching layers like CDN returns the requested data from the nearest proxy server without having to travel to the origin server
Reduce Database load: Implementing various layers from application layer to database caching, number queries fired is reduced, which will reduce the load on the database server
Caching can be implemented in several layers depending on the type of application and the requirements.
Client level caching
Browsers: Browsers have a cache memory which stores web pages, and assets like css, images when the server responds with cache policy headers. This allows users to access these assets faster.
Client applications: Modern frontend tools like, react query, apollo client, swr offers various data fetching and caching options and reduces server load by caching recently accessed data on the client
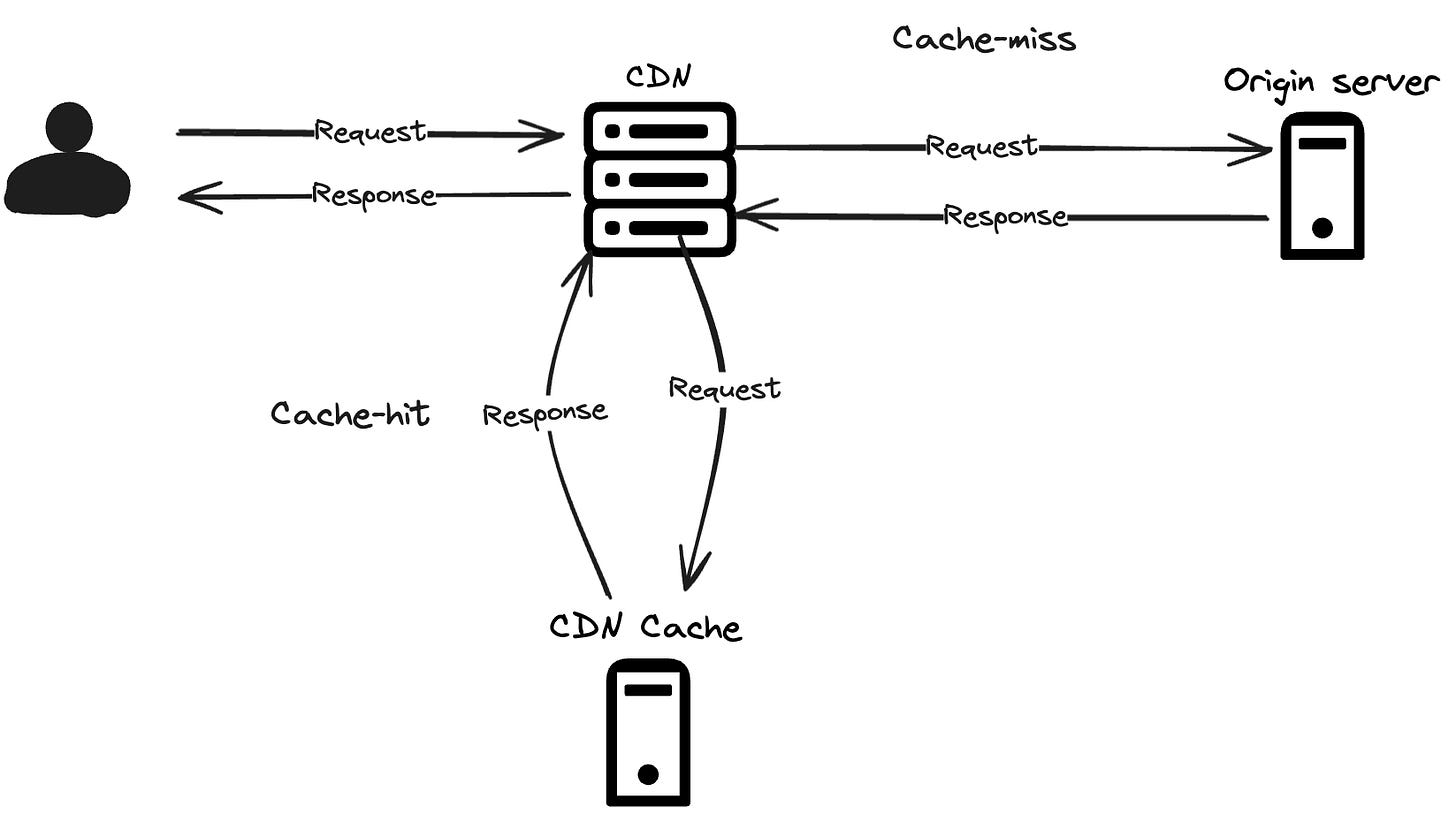
Content Delivery Network or CDN
When a web application is spread across larger regions, the user may access the app from one part of the work while the server might be on the opposite part.
When a user requests for web assets, the CDN retrieves the static assets from the origin server and stores it in a cache proxy server that is close to the user.
Next time when a request is made for the same assets, CDN responds with the cached data instead of requesting the origin server.
CDN is mostly used to caches content like Images, videos, static web pages
Webserver Caching
Typically when a user visits a website, the requests land on web server. It will fire a server side scripting language which will make database calls and builds the requested page once the data is retrieved. Web servers like apache, nginx can be configured to cache these page for future users and return the pages reducing the server load.
Database caching
Firing database queries too frequently may cause load on the database server and some queries may take longer time depending on the complexity of the query.
To reduce load on the database, frequently accessed data can me stored in a temporary memory which will reduce the load on the primary database.
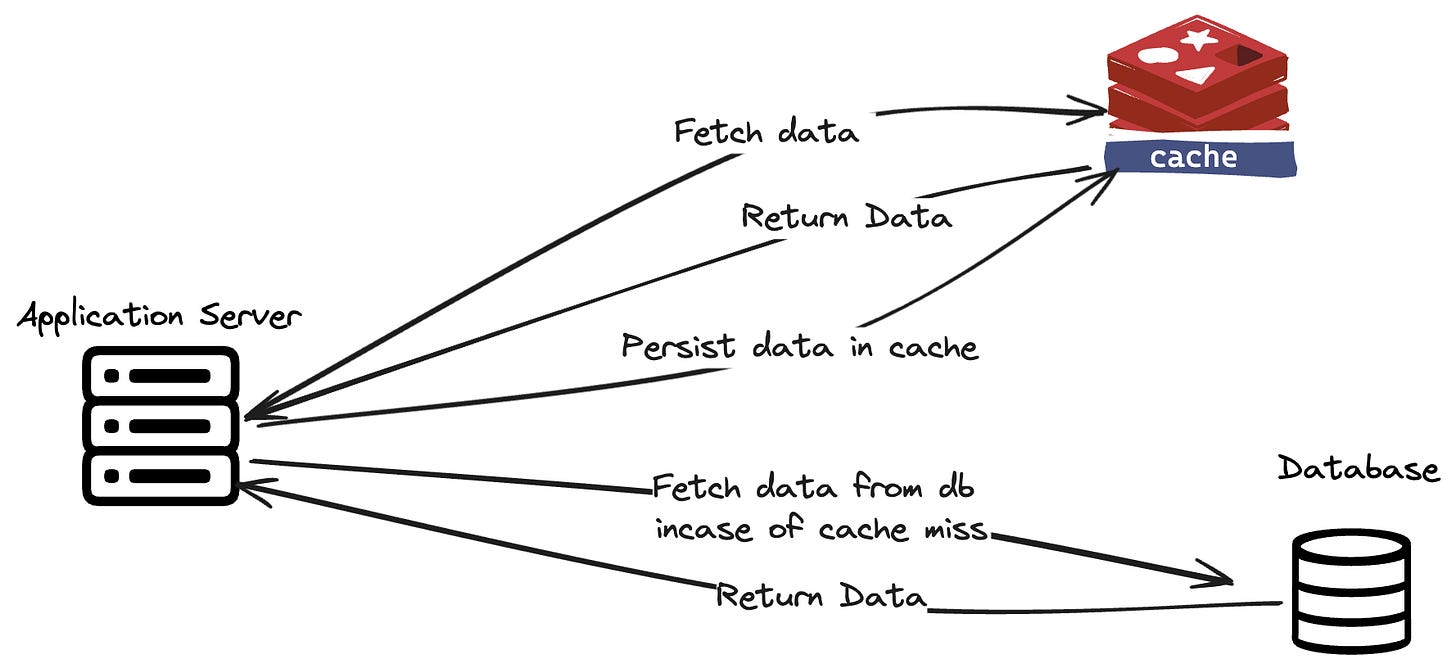
Application caching
Application caching is the most important and the most powerful caching layer. Backend api servers uses in memory databases like redis to store request/response pairs in key value pairs.
This reduces the load on the api and the database as recently accessed data can be directly server from the cached data instead of querying the database.
Caching as a Service
Major Cloud providers provides different ways of caching services depending on your use cases. Some of them are:
Amazon ElastiCache: It supports two in-memory caching engines Redis and MemCache.
Amazon CloudFront: Provides distributed network of proxy servers to cache your static and dynamic content.
DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX): fully managed, highly available, in-memory cache for DynamoDB that delivers up to a 10x performance improvement
Azure Cache for Redis: fully-managed in-memory cache that enables high-performance and scalable architectures
While there are lots of benefits of caching from reducing load on the server and database, reduce response time and reduct costs, not all web application needs to use all layers of caching.
The need for different caching layers changes based on the type of the application you're building.
Cloud News from around the Communitty
Generate AWS CloudFormation templates and AWS CDK apps for existing AWS resources in minutes. You can now generates Cloudformation templates and CDK apps from your existing cloud resources that is outside the cloudformation.
Cloudflare acquires Baselime to expand serverless application observability capabilities
Thanks for reading. See you in the next episode.